Table of Contents
Unveiling Acetate: A Remarkable Compound with Diverse Functions and Impact
Introduction:
Have you ever imagined a basic chemical compound like Acetate could be incredibly versatile? With the formula C2H3O2−, Acetate is a true multitasker, enhancing our lives by adding color, comfort, and style! In this enjoyable and enlightening article, we’ll delve into the captivating world of Acetate, examining its structure, properties, and various applications – from eyewear to the science behind smelly cheese. So fasten your seatbelts and prepare for an acetate journey!
I. Acetate’s Foundations:
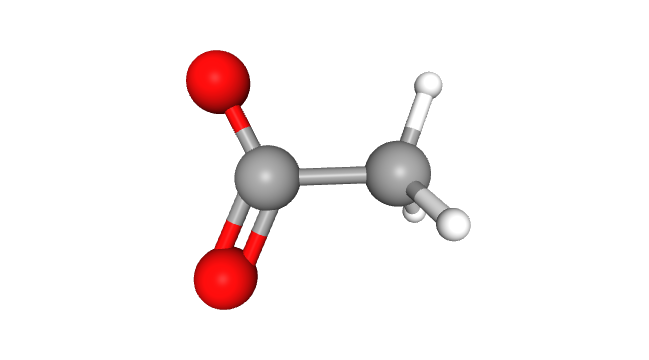
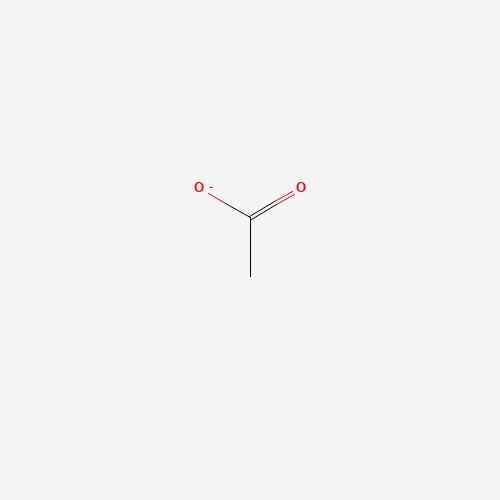
Structure and Properties: Acetate may seem complicated but relatively simple. Its structure includes a methyl group (-CH3) attached to a carbonyl carbon. The carbonyl group is linked to another negatively charged oxygen and the methyl group. But there’s more! Acetate has a hidden power called resonance, enabling equal negative charge distribution across both oxygen atoms, making it a stable and dependable compound.
II. Acetate:
The Fermentation Champion: Acetate is a natural result of fermentation, meaning it has a significant role in some of our most beloved foods and beverages. Within the microscopic realm, methanogenic archaea (tiny microbes) break down Acetate, releasing carbon dioxide and methane gas, which contribute to the delightful fluffiness of bread and the characteristic fizz of champagne. A toast to Acetate!
III. Acetate’s Chemical Adaptability:
Acetate is versatile, reacting with different substances to produce various products. For instance, when Acetate reacts with sodium hydroxide, it generates methane and sodium carbonate through a process called decarboxylation. Also, when Acetate reacts with water, it forms a slightly alkaline solution that can neutralize acidic materials.
IV. Acetate’s Impressive Track Record: Numerous Uses
Spotlight on Acetate! Acetate is a solvent in paints, inks, and coatings, bringing vibrant colors to movies, ads, and artwork.
Stylish Spectacles: Acetate is converted into cellulose acetate, used for eyeglass frames, making them lightweight, fashionable, and long-lasting.
Diaper Duty: Acetate is a key component in diapers, ensuring babies stay dry and comfy.
Preserving Food: Potassium acetate is a food preservative that maintains the taste and freshness of our favorite snacks and goodies.
Laboratory Sidekick: Acetate is a reliable helper in labs, assisting scientists in carrying out experiments and making important discoveries.
Skin Relief: Aluminum acetate provides astringent properties that help alleviate skin irritations and rashes.
V. Acetate:
The Uncelebrated Hero of Human Biochemistry: Acetate also plays a vital role within our bodies besides its numerous external uses. As a building block for biosynthesis, Acetate participates in processes such as fatty acid synthesis. Produced by gut bacteria and obtained from our food, Acetate is converted into acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), which participates in lipid, protein, and carbohydrate metabolism. So the next time you savor a tasty meal, remember to appreciate Acetate’s behind-the-scenes efforts!
Conclusion: Acetate might not be a familiar name, but it is undoubtedly a vital substance with various engaging uses. From the science behind your favorite treats to the fashionable eyeglasses you sport, Acetate is a true hidden gem in our everyday lives. Its diverse uses span from industry to human biology, acting as a fundamental building block for many metabolic pathways and contributing to energy production. So the next time you encounter Acetate in any form, take a moment to recognize its incredible versatility and the numerous ways it enriches our lives. Here’s to Acetate – the essential, amusing, and remarkable compound!
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs: The Fun Edition 
Q1: What’s the story with acetate? 
A: Acetate is like a party animal made of metal cations and acetate anions, which are polyatomic ions. They’re like a little family with two carbon atoms, three hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms (Symbol: CH3COO) – all happily dancing around with a total formula weight of 59.05.
Q2: Acetate vs. Acetic Acid: What’s the deal? 
A: Picture acetic acid as a neutral neighbor, while acetate is the charged-up cousin with a net negative electric charge. Acetic acid is the cool organic compound responsible for creating vinegar, while acetate ion is the wingman, acting as acetic acid’s conjugate base.
Q3: Acetate: Base or acid? 
A: Sodium acetate is like the superhero of basic salts! It swoops in and deprotonates water, raising the pH of the solution. This powerful basic salt is formed through a thrilling showdown between a strong base and a weak acid.
Q4:What are its superpowers? 
A: Acetate fabric is a flexible fashionista with an impressive resistance to wrinkles. ADVANTAGES: Acetate struts its silky appearance and luxurious feel down the runway. DISADVANTAGES: It can be a bit of a drama queen with fading dyes and heat sensitivity. For a happy life together, hand wash your acetate clothes with warm water and a gentle detergent.
Q5: How is acetate born? 
A: This fiber emerges from a magical reaction between acetic anhydride and high-purity wood pulp. Acetate flakes are born from this chemical union, and they dissolve in a solvent, get filtered, and transform into a spinning solution. As a member of the fabulous carboxylate family, acetate anion is a conjugate base of acetic acid. Acetic acid becomes acetate when the pH rises above 5.5, and it’s often found hanging out with organisms in the form of acetyl coenzyme A. Interestingly, acetate produced by oxidizing ethanol is rumored to be the sneaky culprit behind hangovers.
Check Our Chemistry Blog Here: Unravel the Secrets of Chemistry with Engaging Articles
Click Here to Dive Back into Our Educational Resources and Expand Your Knowledge Blog